Getting the Release
The PIO code is currently stored on github at https://github.com/PARALLELIO/ParallelIO. For questions about downloading or developing this code, consult the CIME Git Wiki or email jedwards@ucar.edu.
Download the latest release from the GitHub releases page. Download the release tarball, which will be named something like pio-2.4.3.tar.gz.
Dependencies
PIO can use NetCDF (version 4.6.1+) and/or PnetCDF (version 1.9.0+) for I/O. Ideally, the NetCDF version should be built with MPI, which requires that it be linked with an MPI-enabled version of HDF5. Optionally, NetCDF can be built with DAP support, which introduces a dependency on CURL. Additionally, HDF5, itself, introduces dependencies on LIBZ and (optionally) SZIP.
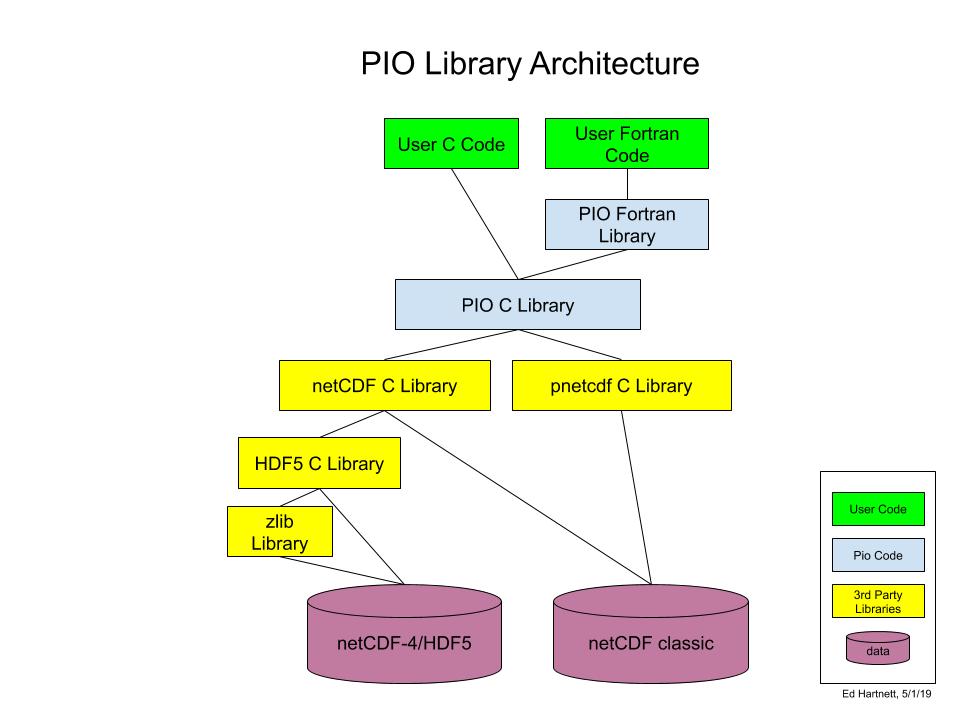
Building PIO C and Fortran Libraries
Unpack the tarball and build with:
./configure --enable-fortran make make check make install
Environment flags CC and FC should be set to MPI C and Fortran compilers. CPPFLAGS may be set to a list of directories which have the include files for netCDF and pnetcdf. LDFLAGS may be set to a list of directories where libraries may be found.
A complete example:
export CPPFLAGS='-I/usr/local/pnetcdf-1.11.0_shared/include -I/usr/local/netcdf-c-4.7.0_hdf5-1.10.5_mpich-3.2/include -I/usr/local/netcdf-fortran-4.4.5_c_4.6.3_mpich-3.2/include' export LDFLAGS='-L/usr/local/pnetcdf-1.11.0_shared/lib -L/usr/local/netcdf-c-4.7.0_hdf5-1.10.5_mpich-3.2/lib' export CC=mpicc export FC=mpifort export CFLAGS='-g -Wall' ./configure --enable-fortran make check make install
#
Testing with MPI
The tests are run as a bash script with called mpiexec to launch programs. If this will not work for the install system, use the –disable-test-runs option to configure. This will cause the tests to be built, but not run. The tests may be run them manually.
Optional GPTL Use
PIO may optionally be built with the General Purpose Timing Library (GPTL). This is necessary for the performance testing program pioperf, but optional for the rest of the library and tests. To build with GPTL, include a path to its include and lib directories in the CPPFLAGS/LDFLAGS flags before running configure.
PIO Library Logging
If built with –enable-logging, the PIO libraries will output logging statements to files (one per task) and stdout. Use the PIOc_set_log_level() function to turn on logging. This will have a negative impact on performance, when used, but helps with debugging.
Building with CMake
A CMake build system is also avaible for the PIO C and Fortran libraries. User may prefer to use a CMake build instead of the autotools build.
To configure the build, PIO requires CMake version 2.8.12+. The typical configuration with CMake can be done as follows:
> CC=mpicc FC=mpif90 cmake [-DOPTION1=value1 -DOPTION2=value2 ...] /path/to/pio/source
where mpicc and mpif90 are the appropriate MPI-enabled compiler wrappers for your system.
The OPTIONS section typically should consist of pointers to the install locations for various dependencies, assuming these dependencies are not located in canonical search locations.
For each dependency XXX, one can specify the location of its installation path with the CMake variable XXX_PATH. If the C and Fortran libraries for the dependency are installed in different locations (such as can be done with NetCDF), then you can specify individually XXX_C_PATH and XXX_Fortran_PATH. Hence, you can specify the locations of both NetCDF-C and NetCDF-Fortran, as well as PnetCDF, with the following CMake configuration line:
> CC=mpicc FC=mpif90 cmake -DNetCDF_C_PATH=/path/to/netcdf-c \
-DNetCDF_Fortran_PATH=/path/to/netcdf-fortran \
-DPnetCDF_PATH=/path/to/pnetcdf \
/path/to/pio/source
This works for the dependencies: NetCDF, PnetCDF, HDF5, LIBZ, SZIP.
For specific instructions to install on various commonly used super computers, please read the walk-through guide to PIO Installation.
Additional CMake Options
Additional configuration options can be specified on the command line.
The PIO_ENABLE_TIMING option can be set to ON or OFF to enable or disable the use of GPTL timing in the PIO libraries. This feature requires the GPTL C library for the PIO C library and the GPTL Fortran library with the perf_mod.mod and perf_utils.mod interface modules. If these GPTL libraries are already installed on the system, the user can point PIO to the location of these libraries with the GPTL_PATH variable (or, individually, GPTL_C_PATH and GPTL_Fortran_Perf_PATH variables). However, if these GPTL libraries are not installed on the system, and GPTL cannot be found, then PIO will build its own internal version of GPTL.
If PnetCDF is not installed on the system, the user can disable its use by setting -DWITH_PNETCDF=OFF. This will disable the search for PnetCDF on the system and disable the use of PnetCDF from within PIO.
If the user wishes to disable the PIO tests, then the user can set the variable -DPIO_ENABLE_TESTS=OFF. This will entirely disable the CTest testing suite, as well as remove all of the test build targets.
If you wish to install PIO in a safe location for use later with other software, you may set the CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX variable to point to the desired install location.
Building with CMake
Once you have successfully configured PIO with CMake in a build directory. From within the build directory, build PIO with:
> make
This will build the pioc and piof libraries.
Testing with CMake
If you desire to do testing, and PIO_ENABLE_TESTS=ON (which is the default setting), you may build the test executables with:
> make tests
Once the tests have been built, you may run tests with:
> ctest
Note: If you have not run make tests before you run ctest, then you will see all of the tests fail.
Alternatively, you may build the test executables and then run tests immediately with:
> make check
(similar to the typical make check Autotools target).
ANOTHER NOTE:* These tests are designed to run in parallel. If you are on one of the supported supercomputing platforms (i.e., NERSC, NWSC, ALCF, etc.), then the ctest command will assume that the tests will be run in an appropriately configured and scheduled parallel job. This can be done by requesting an interactive session from the login nodes and then running ctest from within the interactive terminal. Alternatively, this can be done by running the ctest command from a job submission script. It is important to understand, however, that ctest itself will preface all of the test executable commands with the appropriate mpirun/mpiexec/runjob/etc. Hence, you should not further preface the ctest command with these MPI launchers.
Installing with CMake
Once you have built the PIO libraries, you may install them in the location specified by the CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX. To do this, simply type:
> make install
If the internal GPTL libraries were built (because GPTL could not be found and the PIO_ENABLE_TIMING variable is set to ON), then these libraries will be installed with PIO.
CMake Build Examples
From within the build directory, build the PIO examples with:
> make examples
This will build the C and Fortran examples in under the examples subdirectory.
 1.8.17
1.8.17