CAM5 Scientific Guide¶
- 1. Acknowledgments
- 2. Introduction
- 3. Coupling of Dynamical Core and Parameterization Suite
- 4. Dynamics
- 4.1. Finite Volume Dynamical Core
- 4.1.1. Overview
- 4.1.2. The governing equations for the hydrostatic atmosphere
- 4.1.3. Horizontal discretization of the transport process on the sphere
- 4.1.4. A vertically Lagrangian and horizontally Eulerian control-volume discretization of the hydrodynamics
- 4.1.5. Optional diffusion operators in CAM5
- 4.1.6. A mass, momentum, and total energy conserving mapping algorithm
- 4.1.7. A geopotential conserving mapping algorithm
- 4.1.8. Adjustment of pressure to include change in mass of water vapor
- 4.1.9. Negative Tracer Fixer
- 4.1.10. Global Energy Fixer
- 4.1.11. Further discussion
- 4.1.12. Specified Dynamics Option
- 4.1.13. Further discussion
- 4.2. Spectral Element Dynamical Core
- 4.2.1. Continuum Formulation of the Equations
- 4.2.2. Conserved Quantities
- 4.2.3. Horizontal Discretization: Functional Spaces
- 4.2.4. Horizontal Discretization: Differential Operators
- 4.2.5. Horizontal Discretization: Discrete Inner-Product
- 4.2.6. Horizontal Discretization: The Projection Operators
- 4.2.7. Horizontal Discretization: Galerkin Formulation
- 4.2.8. Vertical Discretization
- 4.2.9. Discrete formulation: Dynamics
- 4.2.10. Consistency
- 4.2.11. Time Stepping
- 4.2.12. Dissipation
- 4.2.13. Discrete formulation: Tracer Advection
- 4.2.14. Conservation and Compatibility
- 4.3. Eulerian Dynamical Core
- 4.3.1. Generalized terrain-following vertical coordinates
- 4.3.2. Conversion to final form
- 4.3.3. Continuous equations using
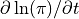
- 4.3.4. Semi-implicit formulation
- 4.3.5. Energy conservation
- 4.3.6. Horizontal diffusion
- 4.3.7. Finite difference equations
- 4.3.8. Time filter
- 4.3.9. Spectral transform
- 4.3.10. Spectral algorithm overview
- 4.3.11. Combination of terms
- 4.3.12. Transformation to spectral space
- 4.3.13. Solution of semi-implicit equations
- 4.3.14. Horizontal diffusion
- 4.3.15. Initial divergence damping
- 4.3.16. Transformation from spectral to physical space
- 4.3.17. Horizontal diffusion correction
- 4.3.18. Semi-Lagrangian Tracer Transport
- 4.3.19. Mass fixers
- 4.3.20. Energy Fixer
- 4.3.21. Statistics Calculations
- 4.3.22. Reduced grid
- 4.4. Semi-Lagrangian Dynamical Core
- 4.4.1. Introduction
- 4.4.2. Vertical coordinate and hydrostatic equation
- 4.4.3. Semi-implicit reference state
- 4.4.4. Perturbation surface pressure prognostic variable
- 4.4.5. Extrapolated variables
- 4.4.6. Interpolants
- 4.4.7. Continuity Equation
- 4.4.8. Thermodynamic Equation
- 4.4.9. Momentum equations
- 4.4.10. Development of semi-implicit system equations
- 4.4.11. Trajectory Calculation
- 4.4.12. Mass and energy fixers and statistics calculations
- 4.1. Finite Volume Dynamical Core
- 5. Model Physics
- 5.1. Conversion to and from dry and wet mixing ratios for trace constituents in the model
- 5.2. Deep Convection
- 5.3. Evaporation of convective precipitation
- 5.4. Prognostic Condensate and Precipitation Parameterization
- 5.5. Cloud Microphysics
- 5.5.1. Overview of the microphysics scheme
- 5.5.2. Radiative Treatment of Ice
- 5.5.3. Formulations for the microphysical processes
- 5.5.3.1. Activation of cloud droplets
- 5.5.3.2. Primary ice nucleation
- 5.5.3.3. Deposition/sublimation of ice
- 5.5.3.4. Conversion of cloud water to rain
- 5.5.3.5. Conversion of cloud ice to snow
- 5.5.3.6. Other collection processes
- 5.5.3.7. Freezing of cloud droplets and rain and ice multiplication
- 5.5.3.8. Melting of cloud ice and snow
- 5.5.3.9. Evaporation/sublimation of precipitation
- 5.5.3.10. Sedimentation of cloud water and ice
- 5.5.3.11. Convective detrainment of cloud water and ice
- 5.5.3.12. Numerical considerations
- 5.6. Parameterization of Cloud Fraction
- 5.7. Aerosols
- 5.8. Condensed Phase Optics
- 5.9. Radiative Transfer
- 5.10. Surface Exchange Formulations
- 5.11. Dry Adiabatic Adjustment
- 5.12. Prognostic Greenhouse Gases
- 6. Extensions to CAM
- 6.1. Introduction
- 6.2. Chemistry
- 6.3. Photolytic Approach (Neutral Species)
- 6.4. Numerical Solution Approach
- 6.5. Superfast Chemistry
- 6.6. Physical Parameterizations
- 6.6.1. Domain and Resolution
- 6.6.2. Molecular Diffusion and Constituent Separation
- 6.6.3. Gravity Wave Drag
- 6.6.4. Turbulent Mountain Stress
- 6.6.5. QBO Forcing
- 6.6.6. Radiation
- 6.6.7. chemistry
- 6.6.8. Electric Field
- 6.6.8.1. Low- and midlatitude electric potential model
- 6.6.8.2. High–latitude electric potential model
- 6.6.8.3. Combing low–/ mid–latitude with the high latitude electric potential
- 6.6.8.4. Calculation of electric field
- 6.6.8.5. Calculation of electrodynamic drift velocity
- 6.6.8.6. Ion drag calculation
- 6.6.9. Boundary Conditions
- 7. Slab Ocean Model
- 8. Sea Ice Thermodynamics
- 9. Initial and Boundary Data
 Flux
Flux