This notebook is adapted from the DART-CAM6 example notebook on AWS
https://
ncar -dart -cam6 .s3 -us -west -2 .amazonaws .com /examples /plot -ensemble -values .html
Input Data Access¶
This notebook illustrates how to make diagnostic plots hosted from the DART reanalysis stored on NCAR’s GDEX
This data is open access and can be accessed via 2 protocols
HTTPS (if you have access to NCAR’s HPC)
OSDF using an intake-ESM catalog.
# Imports
import intake
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import xarray as xr
import seaborn as sns
import re
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport fsspec.implementations.http as fshttp
from pelicanfs.core import PelicanFileSystem, PelicanMap, OSDFFileSystem import dask
from dask_jobqueue import PBSCluster
from dask.distributed import Client
from dask.distributed import performance_reportinit_year0 = '1991'
init_year1 = '2020'
final_year0 = '2071'
final_year1 = '2100'# Set up your scratch folder path
username = os.environ["USER"]
glade_scratch = "/glade/derecho/scratch/" + username
print(glade_scratch)/glade/derecho/scratch/harshah
catalog_url = 'https://osdata.gdex.ucar.edu/d345001/catalogs/d345001-osdf.json'
# catalog_url = 'https://osdata.gdex.ucar.edu/d345001/catalogs/d345001-https.json' #NCAR's Object store
print(catalog_url)https://osdata.gdex.ucar.edu/d345001/catalogs/d345001-osdf.json
Create a PBS cluster¶
# Create a PBS cluster object
cluster = PBSCluster(
job_name = 'dask-wk24-hpc',
cores = 1,
memory = '8GiB',
processes = 1,
local_directory = glade_scratch+'/dask/spill',
log_directory = glade_scratch + '/dask/logs/',
resource_spec = 'select=1:ncpus=1:mem=8GB',
queue = 'casper',
walltime = '5:00:00',
#interface = 'ib0'
interface = 'ext'
)/glade/u/home/harshah/venvs/osdf/lib/python3.10/site-packages/distributed/node.py:187: UserWarning: Port 8787 is already in use.
Perhaps you already have a cluster running?
Hosting the HTTP server on port 36605 instead
warnings.warn(
# Create the client to load the Dashboard
client = Client(cluster)
n_workers = 8
cluster.scale(n_workers)
client.wait_for_workers(n_workers = n_workers)
clusterLoading...
Load DART Reanalysis data from GDEX using an intake catalog¶
col = intake.open_esm_datastore(catalog_url)
colLoading...
Load data into xarray using catalog¶
data_var = 'PS'
col_subset = col.search(variable=data_var)
col_subsetLoading...
col_subset.df['path'].valuesarray(['osdf:///ncar-gdex/d345001/weekly/PS.zarr'], dtype=object)col_subset.dfLoading...
Convert catalog subset to a dictionary of xarray datasets, and use the first one.¶
dsets = col_subset.to_dataset_dict(zarr_kwargs={"consolidated": True})
print(f"\nDataset dictionary keys:\n {dsets.keys()}")
# Load the first dataset and display a summary.
dataset_key = list(dsets.keys())[0]
ds = dsets[dataset_key]
ds
--> The keys in the returned dictionary of datasets are constructed as follows:
'variable.frequency.component.vertical_levels'
Loading...
Loading...
Dataset dictionary keys:
dict_keys(['PS.weekly.atm.1'])
Loading...
# Load the first dataset and display a summary.
dataset_key = list(dsets.keys())[0]
store_name = dataset_key + ".zarr"
ds = dsets[dataset_key]
dsLoading...
Define Plot Functions¶
Get consistently shaped data slices for both 2D and 3D variables.¶
def getSlice(ds, data_var):
'''If the data has vertical levels, choose the level closest
to the Earth's surface for 2-D diagnostic plots.
'''
data_slice = ds[data_var]
if 'lev' in data_slice.dims:
lastLevel = ds.lev.values[-1]
data_slice = data_slice.sel(lev = lastLevel)
data_slice = data_slice.squeeze()
return data_sliceGet lat/lon dimension names¶
def getSpatialDimensionNames(data_slice):
'''Get the spatial dimension names for this data slice.
'''
# Determine lat/lon conventions for this slice.
lat_dim = 'lat' if 'lat' in data_slice.dims else 'slat'
lon_dim = 'lon' if 'lon' in data_slice.dims else 'slon'
return [lat_dim, lon_dim]Produce Time Series Spaghetti Plot of Ensemble Members¶
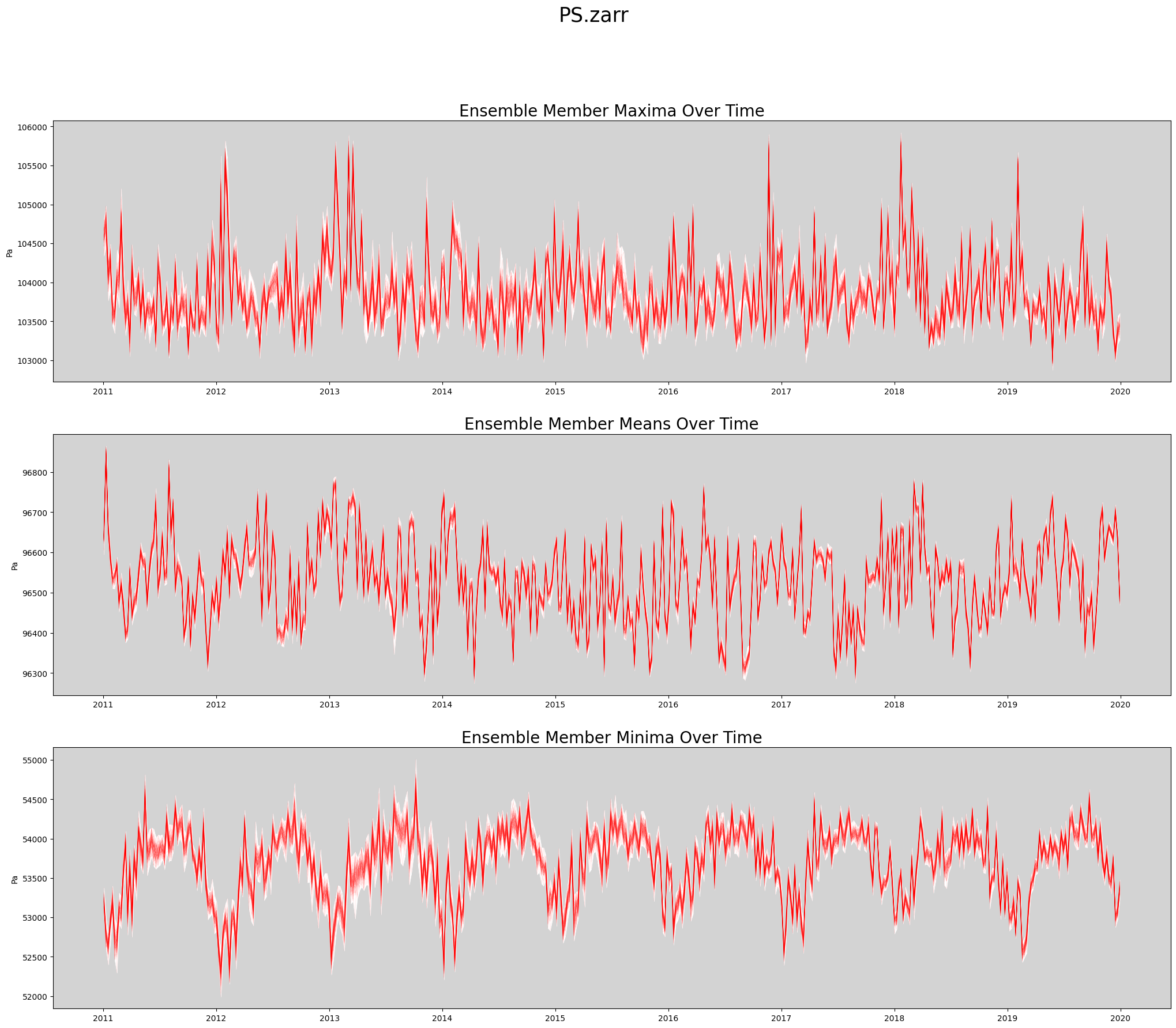
def plot_timeseries(ds, data_var, store_name):
'''Create a spaghetti plot for a given variable.
'''
figWidth = 25
figHeight = 20
linewidth = 0.5
numPlotsPerPage = 3
numPlotCols = 1
# Plot the aggregate statistics across time.
fig, axs = plt.subplots(3, 1, figsize=(figWidth, figHeight))
data_slice = getSlice(ds, data_var)
spatial_dims = getSpatialDimensionNames(data_slice)
unit_string = ds[data_var].attrs['units']
# Persist the slice so it's read from disk only once.
# This is faster when data values are reused many times.
data_slice = data_slice.persist()
max_vals = data_slice.max(dim = spatial_dims).transpose()
mean_vals = data_slice.mean(dim = spatial_dims).transpose()
min_vals = data_slice.min(dim = spatial_dims).transpose()
rangeMaxs = max_vals.max(dim = 'member_id')
rangeMins = max_vals.min(dim = 'member_id')
axs[0].set_facecolor('lightgrey')
axs[0].fill_between(ds.time, rangeMins, rangeMaxs, linewidth=linewidth, color='white')
axs[0].plot(ds.time, max_vals, linewidth=linewidth, color='red', alpha=0.1)
axs[0].set_title('Ensemble Member Maxima Over Time', fontsize=20)
axs[0].set_ylabel(unit_string)
rangeMaxs = mean_vals.max(dim = 'member_id')
rangeMins = mean_vals.min(dim = 'member_id')
axs[1].set_facecolor('lightgrey')
axs[1].fill_between(ds.time, rangeMins, rangeMaxs, linewidth=linewidth, color='white')
axs[1].plot(ds.time, mean_vals, linewidth=linewidth, color='red', alpha=0.1)
axs[1].set_title('Ensemble Member Means Over Time', fontsize=20)
axs[1].set_ylabel(unit_string)
rangeMaxs = min_vals.max(dim = 'member_id')
rangeMins = min_vals.min(dim = 'member_id')
axs[2].set_facecolor('lightgrey')
axs[2].fill_between(ds.time, rangeMins, rangeMaxs, linewidth=linewidth, color='white')
axs[2].plot(ds.time, min_vals, linewidth=linewidth, color='red', alpha=0.1)
axs[2].set_title('Ensemble Member Minima Over Time', fontsize=20)
axs[2].set_ylabel(unit_string)
plt.suptitle(store_name, fontsize=25)
return figActually Create Spaghetti Plot Showing All Ensemble Members¶
%%time
store_name = f'{data_var}.zarr'
fig = plot_timeseries(ds, data_var, store_name)
CPU times: user 10.6 s, sys: 405 ms, total: 11 s
Wall time: 49.5 s
Release dask workers¶
cluster.close()