Meteorology#
Overview#
This section covers meteorology functions from NCL:
Functions#
dewtemp_trh#
NCL’s dewtemp_trh calculates the dew point temperature given temperature and relative humidity using the equations from John Dutton’s “Ceaseless Wind” (pg. 273-274)[1] and returns a temperature in Kelvin.
Where, for the gas constant of water vapor (\(R_{v}\))of 461.5 \(\frac{J}{K*kg}\) (\(\frac{461.5}{1000 * 4.186} \frac{cal}{g*k}\)), the empirical value of the latent heat (pg. 273, Problem 8.3.1) is:
\(L_{lv} = 597.3 - 0.57(T - 273)\)
So, when \(h\) is the relative humidity, the dew point temperature (pg. 273, Equation 6, solved for as \(T_D\)) is:
\(T_D = \frac{T * L_{lv}}{L_{lv} - R_{v}Tlog(h)}\)
Important Note
To convert from Kelvin to Celsius -273.15 and to convert from Celsius to Kelvin +273.15
Grab and Go#
# Input: Single Value
from geocat.comp import dewtemp
temp_c = 18 # Celsius
relative_humidity = 46.5 # %
dewtemp(temp_c + 273.15, relative_humidity) - 273.15 # Returns in Celsius
np.float64(6.298141316024157)
# Input: List/Array
from geocat.comp import dewtemp
temp_kelvin = [291.15, 274.14, 360.3, 314] # Kelvin
relative_humidity = [46.5, 5, 96.5, 1] # %
dewtemp(temp_kelvin, relative_humidity) - 273.15 # Returns in Celsius
array([ 6.29814132, -35.12955277, 86.22114845, -27.40981025])
daylight_fao56#
NCL’s daylight_fao56 calculates the maximum number of daylight hours as described in the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56 (Chapter 3, Equation 34) [2].
Where the maximum number of daylight hours, \(N\), is:
\(N = \frac{24}{{\pi}} {\omega}_{s}\)
And \({\omega}_{s}\) is the sunset hour angle in radians (Chapter 3, Equation 25) [2] which is calculated from the latitude of the observer on Earth (\(\varphi\)) and the sun’s declination (\(\delta\)):
\({\omega}_{s} = arccos[-tan({\varphi})tan({\delta})]\)
Grab and Go#
# Input: Single Value
from geocat.comp import max_daylight
day_of_year = 246 # Sept. 3
latitude = -20 # 20 Degrees South
max_daylight(day_of_year, latitude)
array([[11.665592]], dtype=float32)
# Input: List/Array
from geocat.comp import max_daylight
# Spring Equinox (March 20), Summer Solstice (June 20), Autumn Equinox (Sept. 22), Winter Solstice (Dec. 21)
days_of_year = [79, 171, 265, 355]
latitudes = 40 # Boulder
max_daylight(days_of_year, latitudes)
array([[11.921149],
[14.843202],
[11.920901],
[ 9.156431]], dtype=float32)
satvpr_temp_fao56#
NCL’s satvpr_temp_fao56 calculates saturation vapor pressure using temperature as described in the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56 (Chapter 3, Equation 11) [2].
Where the saturation vapor pressure, \(e^°\) (kPa), at air temperature \(T\) (°C) is calculated as:
\(e^°(T) = 0.6108 {\exp}[\frac{17.27T}{T + 237.3}]\)
Grab and Go#
# Input: Single Value
from geocat.comp import saturation_vapor_pressure
temp = 50 # Fahrenheit
saturation_vapor_pressure(temp)
array(1.22796262)
# Input: List/Array
from geocat.comp import saturation_vapor_pressure
temp = [33, 50, 100, 212] # Fahrenheit
saturation_vapor_pressure(temp)
array([ 0.63594167, 1.22796262, 6.54556639, 102.21571649])
satvpr_tdew_fao56#
NCL’s satvpr_tdew_fao56 calculates the actual saturation vapor pressure using dewpoint temperature as described in the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56 (Chapter 3, Equation 14) [2].
Where the actual vapor pressure, \(e_{a}\) (kPa), is saturation vapor pressure at a specific dewpoint temperature, \(T_{dew}\) (°C), which is calculated as:
\(e_{a} = e^°(T_{dew}) = 0.6108 {\exp}[\frac{17.27 T_{dew}}{T_{dew} + 237.3}]\)
Grab and Go#
# Input: Single Value
from geocat.comp import actual_saturation_vapor_pressure
temp = 35 # Fahrenheit
actual_saturation_vapor_pressure(temp)
array(0.68898447)
# Input: List/Array
from geocat.comp import actual_saturation_vapor_pressure
temp = [35, 60, 80, 200] # Fahrenheit
actual_saturation_vapor_pressure(temp)
array([ 0.68898447, 1.76730647, 3.49620825, 80.00607017])
satvpr_slope_fao56#
NCL’s satvpr_slope_fao56 calculates the slope of the saturation vapor pressure curve as described in the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56 (Chapter 3, Equation 13) [2].
Where the slope of saturation vapor pressure curve, \({\Delta}\) (kPa), at air temperature \(T\) (°C) is calculated as:
\({\Delta} = \frac{4098 (0.6108 {\exp}[\frac{17.27T}{T + 237.3}])}{(T + 237.3)^2}\)
Grab and Go#
# Input: Single Value
from geocat.comp import saturation_vapor_pressure_slope
temp = 60 # Fahrenheit
saturation_vapor_pressure_slope(temp)
array(0.11322096)
# Input: List/Array
from geocat.comp import saturation_vapor_pressure_slope
temp = [35, 60, 80, 200] # Fahrenheit
saturation_vapor_pressure_slope(temp)
array([0.04941909, 0.11322096, 0.20552235, 2.99770999])
coriolis_param#
NCL’s coriolis_param calculates the Coriolis parameter at a given latitude
The Coriolis parameter (also known as the Coriolis frequency or the Coriolis coefficient) is calculated as twice the rotation rate (\({\Omega}\)) of the Earth times the sine of the latitude (\({\varphi}\))[3]
\(f = 2{\Omega}sin({\varphi})\)
The rotation rate depends on the length of the rotation period of the Earth (T) which is defined as one sidereal day (23 hours and 56 minutes):
\({\Omega} = \frac{2 * {\pi}}{T} = 7.292\text{e-5} \frac{rad}{s}\)
# Input: Single Value
from metpy.calc import coriolis_parameter
from metpy.units import units
latitude = 40 # degrees
coriolis_parameter(latitude * units.degree).magnitude
np.float64(9.374562340818716e-05)
# Input: List/Array
from metpy.calc import coriolis_parameter
from metpy.units import units
latitude = [-20, 40, 65] # degrees
coriolis_parameter(latitude * units.degree).magnitude
array([-4.98810043e-05, 9.37456234e-05, 1.32178012e-04])
relhum#
NCL’s relhum calculates relative humidity given temperature, mixing ratio, and pressure.
The percent of relative humidity (\({\Psi}\)) is based on the original NCL relhum code:
\({\Psi} = w (\frac{p - 0.378 * e_s}{0.622 * e_s}) * 100\)
Where \(w\) is the mass mixing ratio of water vapor and dry air, \(p\) is pressure, and \(e_s\) is the saturation vapor pressure for a given temperature.
The constant 0.622 represents the ratio of the molar mass of water vapor (\(M_w\)) in g/mol and the molar mass of dry air (\(M_d\)) in g/mol:
\(\frac{M_w}{M_d} = \frac{18.02}{28.9634} = 0.622\)
Grab and Go#
# Input: Single Value
from geocat.comp import relhum
temp = 303.15 # Kelvin
mixing_ratio = 0.018
pressure = 101325 # Pa
relhum(temp, mixing_ratio, pressure)
np.float64(68.05239617370448)
# Input: List/Array
from geocat.comp import relhum
temp = [375.15, 303.15, 315.15] # Kelvin
mixing_ratio = [0.5, 0.018, 0.001]
pressure = [100325, 101325, 101400] # Pa
relhum(temp, mixing_ratio, pressure)
array([43.78181802, 68.05239617, 1.92796564])
relhum_ice#
NCL’s relhum_ice calculates relative humidity with respect to ice, given temperature, mixing ratio, and pressure.
First,the approximation of vapor pressure is calculated from the Magnus Form.[4]
\({P_v} = c \exp^{\frac{a * T}{b + T}}\)
Where \(c\) is vapor pressure of water at 0 degrees Celsius (Pa), and \(a\) and \(b\) are saturation vapor pressure coefficient approximations over ice, as defined by the AEDki model.[5]
\(a = 22.571\), \(b = 273.71\), \(c = 6.1128\)
Then, the specific humidity (\(q_{st}\)) is calculated with \(p\) as pressure:
\(q_{st} = \frac{0.622 * P_v}{(p * 0.1) - 0.378 * P_v}\)
The constant 0.622 represents the ratio of the molar mass of vapor (\(M_w\)) and dry air (\(M_d\)) in g/mol:
\(\frac{M_w}{M_d} = \frac{18.02}{28.9634} = 0.622\)
And the 0.378 represents a correction constant where:
\(1 - \frac{M_w}{M_d} = 1 - 0.622 = 0.378\)
The percent of relative humidity (\({\Psi}\)) is calculated with \(w\) as the mixing ratio:
\({\Psi} = 100 * \frac{w}{q_{st}}\)
Grab and Go#
# Input: Single Value
from geocat.comp import relhum_ice
temp = 268.15 # Kelvin
mixing_ratio = 0.0037
pressure = 100000 # Pa
relhum_ice(temp, mixing_ratio, pressure)
np.float64(147.88012516016957)
# Input: List/Array
from geocat.comp import relhum_ice
temp = [268.15, 258.15, 250.15] # Kelvin
mixing_ratio = [0.0037, 0.018, 0.001]
pressure = [100000, 100325, 101325] # Pa
relhum_ice(temp, mixing_ratio, pressure)
array([ 147.88012516, 1756.81983351, 211.26793555])
relhum_water#
NCL’s relhum_water calculates relative humidity with respect to water, given temperature, mixing ratio, and pressure.
First,the approximation of vapor pressure is calculated from the Magnus Tetens form.[6]
\({P_v} = c \exp^{\frac{a (T- 273.16)}{T - b}}\)
Where \(c\) is vapor pressure of water at 0 degrees Celsius (Pa) as defined by the AEDki model[5], and \(a\) and \(b\) are saturation vapor pressure coefficient approximations, as defined by the Magnus Tetens model (Equation 6)[6]
\(a = 17.269\), \(b = 35.86\), \(c = 6.1128\)
Then, the specific humidity (\(q_{st}\)) is calculated with \(p\) as pressure:
\(q_{st} = \frac{0.622 * P_v}{(p * 0.1) - 0.378 * P_v}\)
The constant 0.622 represents the ratio of the molar mass of vapor (\(M_w\)) and dry air (\(M_d\)) in g/mol:
\(\frac{M_w}{M_d} = \frac{18.02}{28.9634} = 0.622\)
And the 0.378 represents a correction constant where:
\(1 - \frac{M_w}{M_d} = 1 - 0.622 = 0.378\)
The percent of relative humidity (\({\Psi}\)) is calculated with \(w\) as the mixing ratio:
\({\Psi} = 100 * \frac{w}{q_{st}}\)
Grab and Go#
# Input: Single Value
from geocat.comp import relhum_water
temp = 315.15 # Kelvin
mixing_ratio = 0.0037
pressure = 100000 # Pa
relhum_water(temp, mixing_ratio, pressure)
np.float64(7.025120800518423)
# Input: List/Array
from geocat.comp import relhum_ice
temp = [298.15, 315.15, 330.15] # Kelvin
mixing_ratio = [0.0018, 0.0037, 0.001]
pressure = [100325, 100000, 101325] # Pa
relhum_water(temp, mixing_ratio, pressure)
array([9.04879928, 7.0251208 , 0.87910297])
dpres_plevel#
NCL’s dpres_plevel calculates the change in pressure (delta pressure) for each layer in a specified constant pressure level coordinate system while accounting for specified surface and top pressures.
Important Note
Some layers may be assigned missing values if they are fully below the ground (below surface_pressure) or fully above the specified pressure top in NCL. In geocat-comp the surface pressure is accounted for as in NCL, but the pressure top is assumed to be the minimum specified pressure level and is not currently user configurable.
For example:
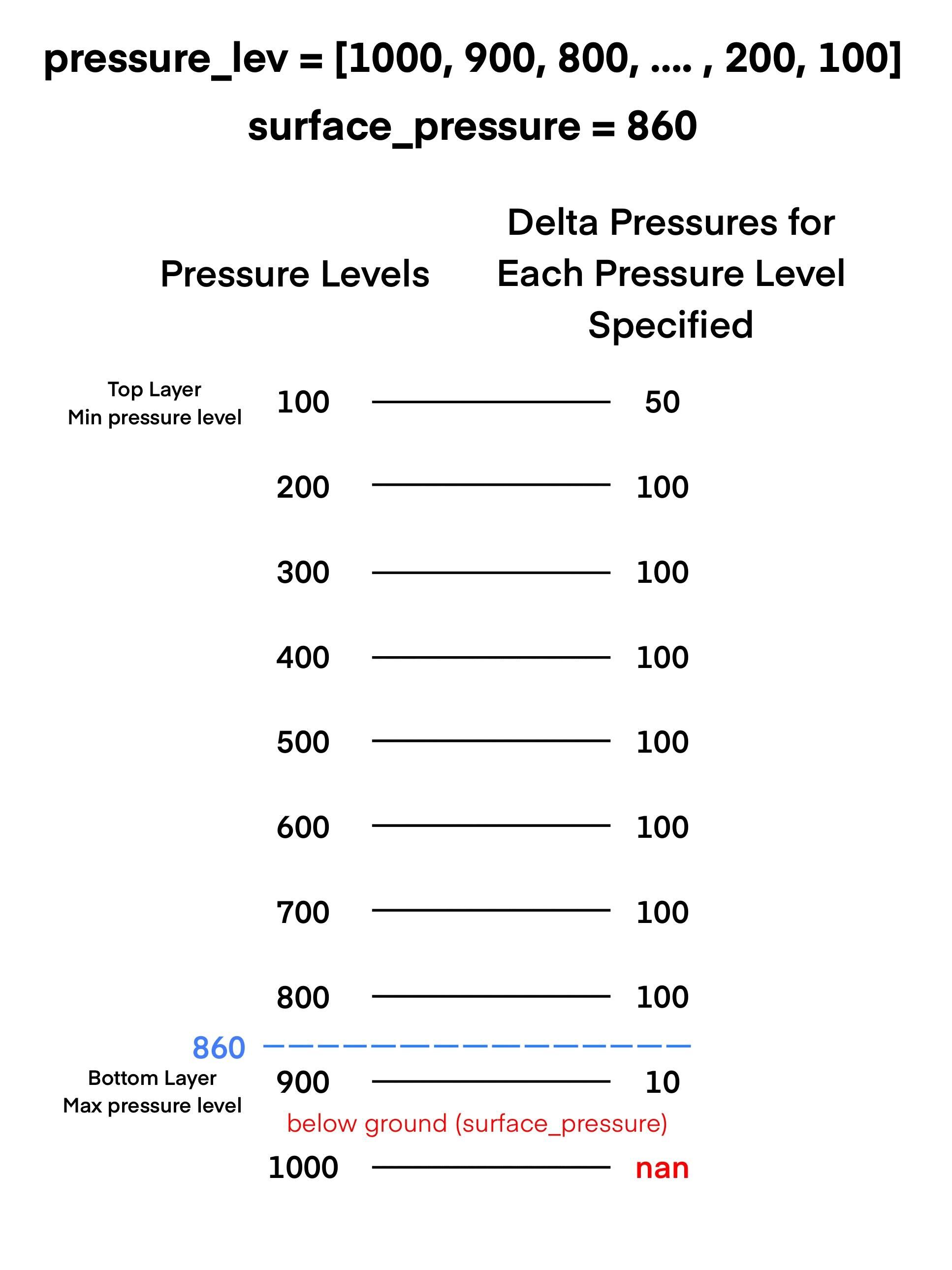
Grab and Go#
# Input: Single Value
from geocat.comp import delta_pressure
import numpy as np
pressure_levels = np.array(
[
1000,
950,
900,
850,
800,
750,
700,
650,
600,
550,
500,
450,
400,
350,
300,
250,
200,
175,
150,
125,
100,
80,
70,
60,
50,
40,
30,
25,
20,
]
)
surface_pressure = 1050
delta_pressure(pressure_levels, surface_pressure)
array([75. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. ,
50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 37.5, 25. , 25. , 25. , 22.5, 15. ,
10. , 10. , 10. , 10. , 7.5, 5. , 2.5])
# Input: List/Array
from geocat.comp import delta_pressure
import numpy as np
pressure_levels = np.array(
[
1000,
950,
900,
850,
800,
750,
700,
650,
600,
550,
500,
450,
400,
350,
300,
250,
200,
175,
150,
125,
100,
80,
70,
60,
50,
40,
30,
25,
20,
]
)
surface_pressure = np.array([1000, 1025, 1050])
delta_pressure(pressure_levels, surface_pressure)
array([[25. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. ,
50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 37.5, 25. , 25. , 25. , 22.5, 15. ,
10. , 10. , 10. , 10. , 7.5, 5. , 2.5],
[50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. ,
50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 37.5, 25. , 25. , 25. , 22.5, 15. ,
10. , 10. , 10. , 10. , 7.5, 5. , 2.5],
[75. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. ,
50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 50. , 37.5, 25. , 25. , 25. , 22.5, 15. ,
10. , 10. , 10. , 10. , 7.5, 5. , 2.5]])
psychro_fao56#
NCL’s psychro_fao56 computes the psychrometric constant (kPa/C) as described in the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56 (Chapter 3, Equation 8 or Equation 3-10 in Annex 3)[2].
\({\gamma} = \frac{c_{p}P}{{\epsilon}{\lambda}}\)
\({\gamma} = \frac{1.013 \text{e-3} * P}{0.622 * 2.45}\)
\({\gamma} = 0.6647 \text{e-3} * P\)
Where, \({\gamma}\) is the psychrometric constant (in kPa/C), \(P\) is the atmospheric pressure (kPa), \({\lambda}\) is the latent heat vaporization (2.45 MJ/kgC), and \({\epsilon}\) is the ratio of the molecular weight of water and dry air (0.622)
Grab and Go#
# Input: Single Value
from geocat.comp import psychrometric_constant
pressure = 80 # kPa/C
psychrometric_constant(pressure)
np.float64(0.0531792)
# Input: List/Array
from geocat.comp import psychrometric_constant
pressure = [10, 50, 80, 1000]
psychrometric_constant(pressure)
array([0.0066474, 0.033237 , 0.0531792, 0.66474 ])
Python Resources#
Additional Reading#
MetPy
relative_humidity_from_mixing_ratioDocumentation with alternative equation
