- This workflow is inspired by https://
gallery .pangeo .io /repos /pangeo -gallery /cmip6 /global _mean _surface _temp .html
Table of Contents¶
Section 1: Introduction¶
- Load python packkages
- Load catalog url
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import xarray as xr
import numpy as np
import dask
from dask.diagnostics import progress
from tqdm.autonotebook import tqdm
import intake
import fsspec
import seaborn as sns
import re
import aiohttp
from dask_jobqueue import PBSCluster
import pandas as pd/glade/derecho/scratch/harshah/tmp/ipykernel_10484/493514256.py:6: TqdmExperimentalWarning: Using `tqdm.autonotebook.tqdm` in notebook mode. Use `tqdm.tqdm` instead to force console mode (e.g. in jupyter console)
from tqdm.autonotebook import tqdm
import fsspec.implementations.http as fshttp
from pelicanfs.core import OSDFFileSystem,PelicanMap lustre_scratch = "/lustre/desc1/scratch/harshah"
#
gdex_url = 'https://data.gdex.ucar.edu/'
cat_url = gdex_url + 'd850001/catalogs/osdf/cmip6-aws/cmip6-osdf-zarr.json'Section 2: Select Dask Cluster¶
Select the Dask cluster type¶
The default will be LocalCluster as that can run on any system.
If running on a HPC computer with a PBS Scheduler, set to True. Otherwise, set to False.
USE_PBS_SCHEDULER = TrueIf running on Jupyter server with Dask Gateway configured, set to True. Otherwise, set to False.
USE_DASK_GATEWAY = FalsePython function for a PBS cluster¶
# Create a PBS cluster object
def get_pbs_cluster():
""" Create cluster through dask_jobqueue.
"""
from dask_jobqueue import PBSCluster
cluster = PBSCluster(
job_name = 'dask-osdf-24',
cores = 1,
memory = '4GiB',
processes = 1,
local_directory = lustre_scratch + '/dask/spill',
log_directory = lustre_scratch + '/dask/logs/',
resource_spec = 'select=1:ncpus=1:mem=4GB',
queue = 'casper',
walltime = '3:00:00',
#interface = 'ib0'
interface = 'ext'
)
return clusterPython function for a Gateway Cluster¶
def get_gateway_cluster():
""" Create cluster through dask_gateway
"""
from dask_gateway import Gateway
gateway = Gateway()
cluster = gateway.new_cluster()
cluster.adapt(minimum=2, maximum=4)
return clusterdef get_local_cluster():
""" Create cluster using the Jupyter server's resources
"""
from distributed import LocalCluster, performance_report
cluster = LocalCluster()
cluster.scale(6)
return clusterPython logic for a Local Cluster¶
This uses True/False boolean logic based on the variables set in the previous cells
# Obtain dask cluster in one of three ways
if USE_PBS_SCHEDULER:
cluster = get_pbs_cluster()
elif USE_DASK_GATEWAY:
cluster = get_gateway_cluster()
else:
cluster = get_local_cluster()
# Connect to cluster
from distributed import Client
client = Client(cluster)/glade/u/home/harshah/venvs/osdf/lib/python3.10/site-packages/distributed/node.py:187: UserWarning: Port 8787 is already in use.
Perhaps you already have a cluster running?
Hosting the HTTP server on port 40697 instead
warnings.warn(
# Scale the cluster and display cluster dashboard URL
cluster.scale(8)
clusterLoading...
Section 3: Data Loading¶
- Load catalog and select data subset
col = intake.open_esm_datastore(cat_url)
colLoading...
[eid for eid in col.df['experiment_id'].unique() if 'ssp' in eid]['esm-ssp585-ssp126Lu',
'ssp126-ssp370Lu',
'ssp370-ssp126Lu',
'ssp585',
'ssp245',
'ssp370-lowNTCF',
'ssp370SST-ssp126Lu',
'ssp370SST',
'ssp370pdSST',
'ssp370SST-lowCH4',
'ssp370SST-lowNTCF',
'ssp126',
'ssp119',
'ssp370',
'esm-ssp585',
'ssp245-nat',
'ssp245-GHG',
'ssp460',
'ssp434',
'ssp534-over',
'ssp245-aer',
'ssp245-stratO3',
'ssp245-cov-fossil',
'ssp245-cov-modgreen',
'ssp245-cov-strgreen',
'ssp245-covid',
'ssp585-bgc']# there is currently a significant amount of data for these runs
expts = ['historical', 'ssp245', 'ssp370']
query = dict(
experiment_id=expts,
table_id='Amon',
variable_id=['tas'],
member_id = 'r1i1p1f1',
#activity_id = 'CMIP',
)
col_subset = col.search(require_all_on=["source_id"], **query)
col_subsetLoading...
col_subset.df.groupby("source_id")[["experiment_id", "variable_id", "table_id","activity_id"]].nunique()Loading...
col_subset.dfLoading...
# %%time
# dsets_osdf = col_subset.to_dataset_dict()
# print(f"\nDataset dictionary keys:\n {dsets_osdf.keys()}")def drop_all_bounds(ds):
drop_vars = [vname for vname in ds.coords
if (('_bounds') in vname ) or ('_bnds') in vname]
return ds.drop_vars(drop_vars)
def open_dset(df):
assert len(df) == 1
mapper = fsspec.get_mapper(df.zstore.values[0])
path = df.zstore.values[0][7:]+".zmetadata"
ds = xr.open_zarr(mapper, consolidated=True)
a_data = mapper.fs.get_access_data()
responses = a_data.get_responses(path)
print(responses)
return drop_all_bounds(ds)
def open_delayed(df):
return dask.delayed(open_dset)(df)
from collections import defaultdict
dsets = defaultdict(dict)
for group, df in col_subset.df.groupby(by=['source_id', 'experiment_id']):
dsets[group[0]][group[1]] = open_delayed(df)dsets_ = dask.compute(dict(dsets))[0]#calculate global means
def get_lat_name(ds):
for lat_name in ['lat', 'latitude']:
if lat_name in ds.coords:
return lat_name
raise RuntimeError("Couldn't find a latitude coordinate")
def global_mean(ds):
lat = ds[get_lat_name(ds)]
weight = np.cos(np.deg2rad(lat))
weight /= weight.mean()
other_dims = set(ds.dims) - {'time'}
return (ds * weight).mean(other_dims)expt_da = xr.DataArray(expts, dims='experiment_id', name='experiment_id',
coords={'experiment_id': expts})
dsets_aligned = {}
for k, v in tqdm(dsets_.items()):
expt_dsets = v.values()
if any([d is None for d in expt_dsets]):
print(f"Missing experiment for {k}")
continue
for ds in expt_dsets:
ds.coords['year'] = ds.time.dt.year
# workaround for
# https://github.com/pydata/xarray/issues/2237#issuecomment-620961663
dsets_ann_mean = [v[expt].pipe(global_mean).swap_dims({'time': 'year'})
.drop_vars('time').coarsen(year=12).mean()
for expt in expts]
# align everything with the 4xCO2 experiment
dsets_aligned[k] = xr.concat(dsets_ann_mean, join='outer',dim=expt_da)Loading...
%%time
with progress.ProgressBar():
dsets_aligned_ = dask.compute(dsets_aligned)[0]CPU times: user 21.9 s, sys: 1.36 s, total: 23.3 s
Wall time: 1min 59s
source_ids = list(dsets_aligned_.keys())
source_da = xr.DataArray(source_ids, dims='source_id', name='source_id',
coords={'source_id': source_ids})
big_ds = xr.concat([ds.reset_coords(drop=True)
for ds in dsets_aligned_.values()],
dim=source_da)
big_dsLoading...
Observational time series data for comparison with ensemble spread¶
- The observational data we will use is the HadCRUT5 dataset from the UK Met Office
- The data has been downloaded to NCAR’s Geoscience Data Exchange (GDEX) from https://
www .metoffice .gov .uk /hadobs /hadcrut5/ - We will use an OSDF file system to access this copy from the GDEX
osdf_fs = OSDFFileSystem()
print(osdf_fs)
#
obs_url = '/ncar/gdex/d850001/HadCRUT.5.0.2.0.analysis.summary_series.global.monthly.nc'
#
obs_ds = xr.open_dataset(osdf_fs.open(obs_url,mode='rb'),engine='h5netcdf').tas_mean
obs_dsLoading...
# obs_url = 'osdf:///ncar/gdex/d850001/HadCRUT.5.0.2.0.analysis.summary_series.global.monthly.zarr'
# print(obs_url)
# #
# obs_ds = xr.open_zarr(obs_url).tas_mean
# # obs_ds# Compute annual mean temperatures anomalies
obs_gmsta = obs_ds.resample(time='YS').mean(dim='time')
obs_gmstaLoading...
Section 4: Data Analysis¶
- Calculate Global Mean Surface Temperature Anomaly (GMSTA)
- Grab some observations/ ERA5 reanalysis data
- Convert xarray datasets to dataframes
- Use Seaborn to plot GMSTA
df_all = big_ds.to_dataframe().reset_index()
df_all.head()Loading...
# Compute anomaly w.r.t 1960-1990 baseline
# Define the baseline period
baseline_df = df_all[(df_all["year"] >= 1960) & (df_all["year"] <= 1990)]
# Compute the baseline mean
baseline_mean = baseline_df["tas"].mean()
# Compute anomalies
df_all["tas_anomaly"] = df_all["tas"] - baseline_mean
df_allLoading...
obs_df = obs_gmsta.to_dataframe(name='tas_anomaly').reset_index()
# obs_df# Convert 'time' to 'year' (keeping only the year)
obs_df['year'] = obs_df['time'].dt.year
# Drop the original 'time' column since we extracted 'year'
obs_df = obs_df[['year', 'tas_anomaly']]
obs_dfLoading...
# Create the main plot
g = sns.relplot(data=df_all, x="year", y="tas_anomaly",
hue='experiment_id', kind="line", errorbar="sd", aspect=2, palette="Set2") # Adjust the color palette)
# Get the current axis from the FacetGrid
ax = g.ax
# Overlay the observational data in red
sns.lineplot(data=obs_df, x="year", y="tas_anomaly",color="red",
linestyle="dashed", linewidth=2,label="Observations", ax=ax)
# Adjust the legend to include observations
ax.legend(title="Experiment ID + Observations")
# Show the plot
plt.show()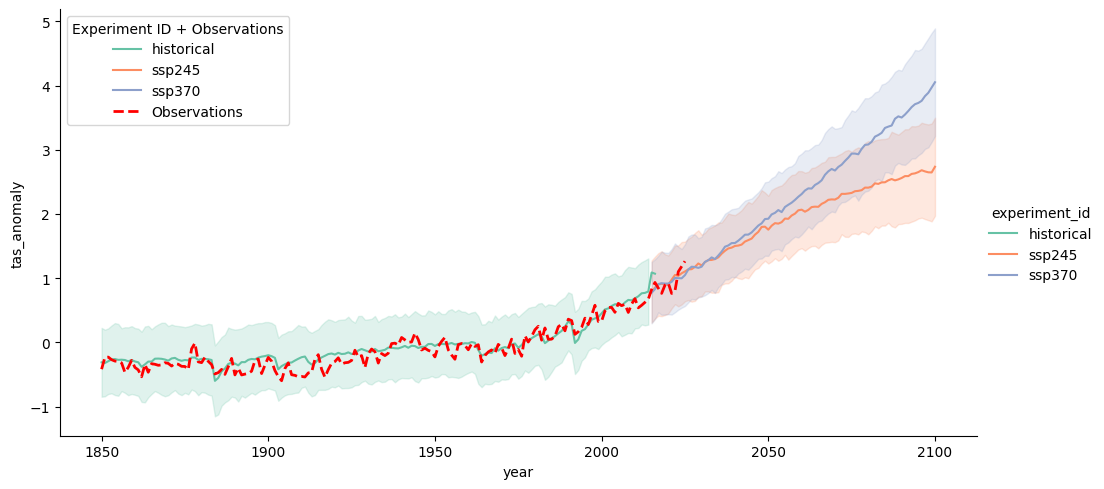
cluster.close()# sns.relplot(data=df_all,x="year", y="tas_anomaly", hue='experiment_id',kind="line", errorbar="sd", aspect=2)