SOPS, Age, and helm-secrets#
We utilize SOPS and age to encrypt sensitive information in our Helm charts in order to include all content required for administrators to deploy our applications via GitHub.
Installation#
Age installation#
You can locate age installation instructions for your OS at this link to the age github repository.
SOPS installation#
You can locate the current binaries and installation instruction at this link to the SOPS github repository.
Helm-secrets installation#
You should reference this link to the helm-secrets github repo for installation instructions and to ensure you are getting the latest stable version.
Getting Started#
First make sure you have your binaries installed correctly by checking their versions:
age -version
age-keygen -version
sops -version
helm plugin list
After validating that the applications are installed and working correctly you can proceed to the setup.
age-keygen#
You need to generate your public and private key pair. The private key needs to be kept secret and never shared with anyone. The public key can be shared with anyone and they could use your public key to send you encrypted information. Reference the SOPS section below to see what default directories SOPS looks for the key. Otherwise export an environment variable of SOPS_AGE_KEY_FILE with your key location.
Setup the public and private key pair with:
age-keygen -o keys.txt
Your public key is printed out when you generate the key pair but it is also a commented entry inside your key file so it’s still available even if you don’t copy the output.
With the key file setup you can now encrypt and decrypt files. You can check the help syntax and start testing with encrypting different files. Reference the documentation on how to utilize age for encryption and decryption.
SOPS#
When decrypting a file with the corresponding identity, sops will look for a text file name keys.txt located in a sops subdirectory of your user configuration directory.
On Linux, this would be $XDG_CONFIG_HOME/sops/age/keys.txt.
On macOS, this would be $HOME/Library/Application Support/sops/age/keys.txt.
On Windows, this would be %AppData%\sops\age\keys.txt.
You can specify the location of this file manually by setting the environment variable SOPS_AGE_KEY_FILE. Alternatively you can provide the the key(s) directly by setting the SOPS_AGE_KEY environment variable.
helm-secrets#
With the prerequisites met, helm should be able to encrypt and decrypt the yaml and json files.
You can test with:
helm secrets edit test.yaml
You should see a sample yaml file generate and you could modify this file and save it if needed.
Usage#
Here you can find a couple examples on how to use the binaries for encryption and decryption.
age#
Encryption can be done with:
age -o example.yaml.age -r
age1ucetgj7k3whaqf9nulacsqarur6nrgzuyt59apeptu5cphd6ksdsqpy5he example-enc.yaml
Decryption can be done by the recipient with:
age -d -o example.yaml example-enc.yaml
SOPS#
Encryption can be done with:
sops --encrypt --age age1yt3tfqlfrwdwx0z0ynwplcr6qxcxfaqycuprpmy89nr83ltx74tqdpszlw example.yaml > example.enc.yaml
Decryption can be done by the recipient with:
sops --decrypt example.enc.yaml > example.yaml
.sops.yaml file#
The .sops.yaml file allows sops to properly encrypt files and data with a regex. This allows us to utilize sops to encrypt secrets in our helm value files and those files can be stored in github. The .sops.yaml file will looks something like this:
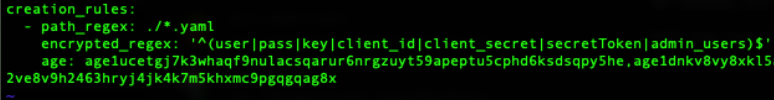
Please reference the SOPS documentation for additional details. This file allows us to use multiple encryption methods with SOPS like KMS services. PGP/GPG is available but it is being deprecated in favor of age.
helm-secrets#
The helm-secrets plugin allows a user to encrypt,decrypt,install, and lint helm value files. The plugin also allows a user to edit encrypted helm files. You need to have the .sops.yaml file created for helm-secrets to operate on encrypted files.
Encryption can be done with:
helm secrets encrypt example.yaml > example-enc.yaml
Decryption can be done with:
helm secrets decrypt example-enc.yaml > example.yaml
Install a chart with:
helm secrets install <deployment-name> <repo/chart> -f example-enc.yaml
Helm-secrets is a wrapper script to helm so all of the helm installations options should be available like setting the namespace and other chart variables.


