Paleo#
Paleoclimatology is the study of ancient climate variability and change, before the availability of instrumental records.
Paleoclimatology relies on a combination of physical, biological, and chemical proxies of past environmental and climate change, such as glacial ice, tree rings, sediments, corals, and cave mineral deposits.
CESM is widely used for paleoclimate studies.
CESM simulations of past climates are a tool to better understand and interpret proxy reconstructions and to evaluate CESM skill in simulating out-of-sample climate states.
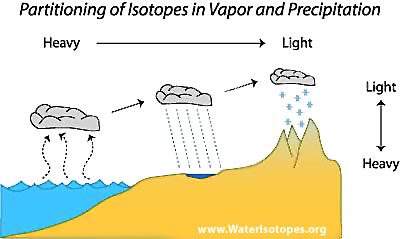
Many proxy reconstructions are made using measurements of isotopic ratios in natural archives.
A version of CESM with the capability to simulate hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratios in the water cycle (isotope-enabled CESM) is commonly used in paleoclimate studies to provide more direct signals of comparison with proxies.
Learning Goals#
Student will learn how to modify Earth’s orbital configuration in CESM for a simple paleoclimate experiment.
Student will learn how to validate that the orbital modification is implemented properly.
Student will learn how to quickly compare differences in paleo and preindustrial CESM runs using NCO and Ncview.
Student will learn how to run a preindustrial isotope-enabled CESM experiment and plot precipitation δ18O.
Exercise 1-2 Details#
This exercise uses the same code base as the rest of the tutorial.
You will be using the B1850 compset at the f19_g17 resolution.
You will run a preindustrial control simulation and a simple mid-Holocene simulation.
Exercise 3 Details#
This exercise uses a different code base from the rest of the tutorial (isotope-enabled CESM1.3).
You will be using the B1850C5 compset at the f19_g16 resolution.
You will run a preindustrial simulation with water isotope tracers.